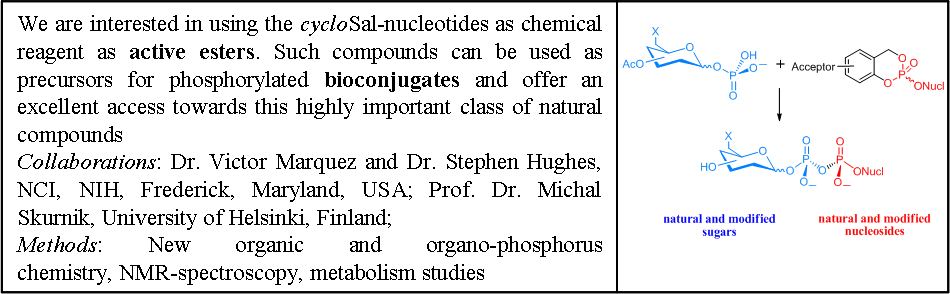CycloSal-Nucleotides as Chemical Reagents
1. Background
The release of a nucleoside monophosphate from a cycloSal-nucleotide is based on an efficient and highly selective chemical hydrolysis pathway. Therefore, cycloSal-nucleotides can also be used, as active esters to gain access to various phosphorylated biomolecules. In contrast to other common pronucleotid concepts that depend on enzymatic activation, the cleavage of the lipophilic mask of a cycloSal-nucleotide 1 is initiated by nucleophilic attack of hydroxide at the phosphate triester. The use of nucleophiles other than hydroxide leads to the formation of the following target molecules:
I) nucleoside 5'-di- and triphosphates
II) nucleoside diphosphate sugars
III) nucleoside monophosphate sugars
IV-VI) dinucleoside polyphosphates
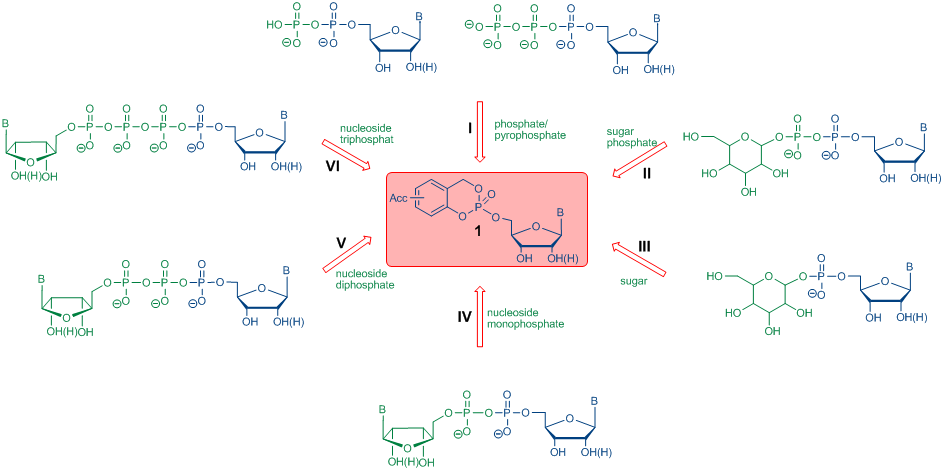 Scheme 1: Synthesis of various phosphorylated biomolecules using cycloSal-nucleotides
Scheme 1: Synthesis of various phosphorylated biomolecules using cycloSal-nucleotidesFor synthetic applications of cycloSal-nucleotides as phosphate active esters acceptor substituted compounds are used to increase the electrophilicity of the phosphorous center and, as a consequence, accelerate the initial reaction that means cleavage of the phenolic phosphate ester bond (Scheme 2, A). Subsequently, the benzylphosphate diester is cleaved selectively to the desired target molecule and after aqueous work up to the salicyl alcohol (Scheme 2, B).
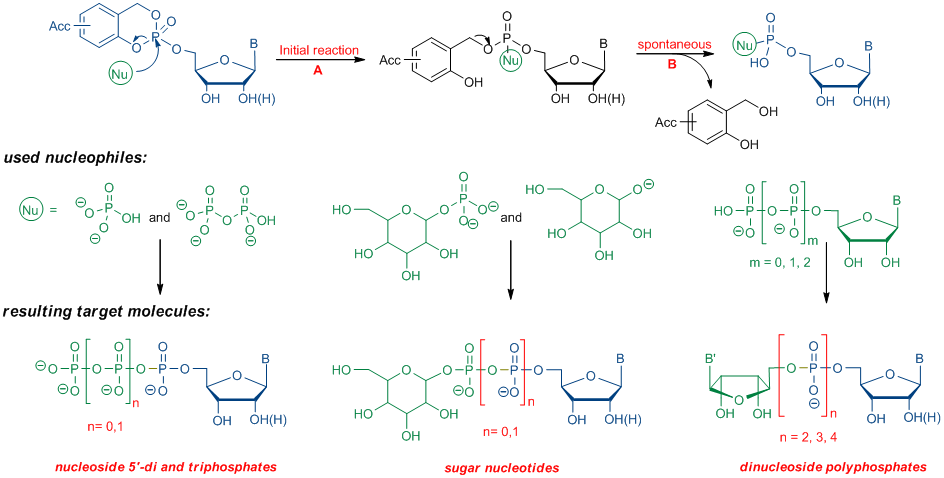 Scheme 2: Nucleophilic cleavage of cycloSal-nucleotides
Scheme 2: Nucleophilic cleavage of cycloSal-nucleotidesRecently, the conversions shown in scheme 2 are carried out on solid-phase, too. Therefore, a cycloSal phosphate triester is at first connected with a linker and afterwards attached to a functionalised solid-support. The attack of a desired nucleophile (see scheme 2) yields in the case of quantitative conversion of the triester pure products after cleavage from the solid-support.
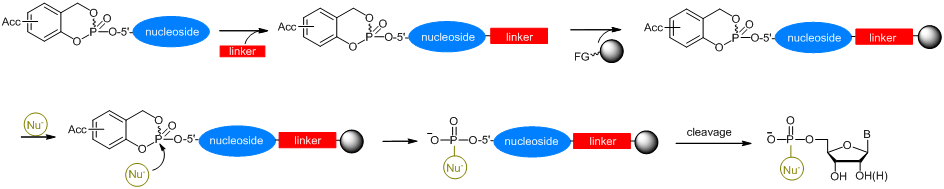 Scheme 3: Solid-support assisted synthesis of 5'-phosphorylated biomolecule
Scheme 3: Solid-support assisted synthesis of 5'-phosphorylated biomolecule2. Biological Importance
a) of nucleoside 5'-triphosphate
Nucleoside 5á-triphosphates (NTPs) represent a class of very important compounds in biological systems. Naturally occurring NTPs serve as building blocks for the enzymatic synthesis of DNA and RNA. Moreover, some analogues are used as diagnostic and therapeutic agents, e.g. as chemotherapeutic agents. In addition, there are a lot of applications of NTPs concerning structure determination of nucleic acids, the use as substrates for DNA and RNA sequencing and for labelling of hybridation. Due to their importance in vivo and in vitro a generally applicable and efficient synthetic strategy for NTPs is needed.
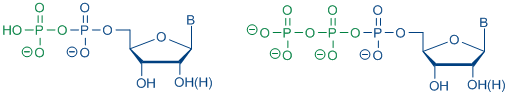 Scheme 4: Structures of ribo- and 2'-deoxyribonucleoside 5'-di- and triphosphate
Scheme 4: Structures of ribo- and 2'-deoxyribonucleoside 5'-di- and triphosphateb) of nucleoside diphosphate pyranoses
Many infections are based on gram-negative bacteria. They are antagonised by antibiotics, whereat there is the possibility of death caused by septic shock. The number of deaths remains constant. The septic shock consists of the Lipoid-A-compound of the LPS which operates as an endotoxine.
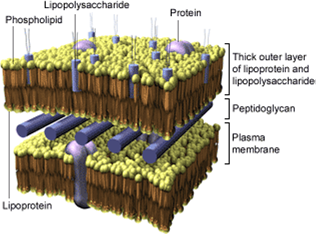
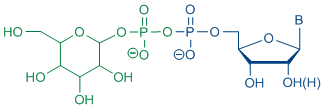
Moreover, after destruction of such bacteria due to antibiotics, the high amount of lipopolysaccharides released is responsible for the development of the septic shock. Therefore, it is of great interest to design antibacterial agents which do not release endotoxines. For this approach an adequate access to nucleoside diphosphate glycopyranoses is required.
Article in the newspaper "Die Welt" on nucleoside diphosphate sugars (21.04.2008): http://www.welt.de/welt_print/article1922164/Trojanische_Pferde_gegen_Krankheiten.html
3. Selected Publications
- S. Wendicke, S. Warnecke, C. Meier, Efficient Synthesis of Nucleoside Diphosphate Glycopyranoses, Angew. Chem. 2008, 120, 1523-1525; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 1500-1502.
- S. Warnecke, C. Meier, Synthesis of Nucleoside Di- and Triphosphates and Dinucleoside Polyphosphates with cycloSal-Nucleotides, J. Org. Chem. 2009, 3024-3030.
- S. Wolf, T. Zismann, N. Lunau, C. Meier, Reliable Synthesis of Various Nucleoside Diphosphate Glycopyranoses, Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 7656-7664.
- S. Wolf, T. Zismann, N. Lunau, S. Warnecke, S. Wendicke, C. Meier, A Convenient Synthesis of Nucleoside Diphosphate Glycopyranoses and Other Polyphosphorylated Bioconjugates, Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 89, 63-75.
- V. C. Tonn, C. Meier, Solid-Phase Synthesis of (Poly)phosphorylated Nucleosides and Conjugates, Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 9832-9842.
- S. Wolf, R. Molina Berrio, C. Meier, Synthesis of Nonnatural Nucleoside Diphosphate Sugars, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 6304-6313.
- N. Lunau, C. Meier, Synthesis of L-Altrose and Some Derivatives, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 6260-6270.
- S. Wolf, S. Warnecke, J. Ehrit, F. Freiberger, R. Gerardy-Schahn, C. Meier, Chemical Synthesis and Enzymatic Testing of CMP-Sialic Acid Derivatives, ChemBioChem 2012, in press.