Diastereoselective synthesis of nucleotide prodrugs

Nucleotide prodrugs are systems which allow the delivery of the nucleoside monophosphate into cells. Due to the high polarity of nucleotides at physiological pH-value, these compounds are unable to penetrate the hydrophobic/lipophilic cell membrane. A number of prodrug systems have been developed in order to mask the two negative charges of the phosphate group. Inside the cell the lipophilic mask should be cleaved by chemical or enzymatical means. The cycloSal-prodrug system developed by us uses salicylalcohol derivatives as lipophilic mask (Figure 1).[1], [2]
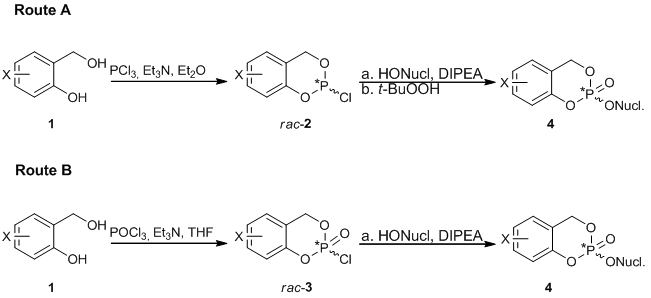 Figure 1: Synthesis of cycloSal-Pronucleotide 4
Figure 1: Synthesis of cycloSal-Pronucleotide 4Due to the non-stereoselective synthesis routes A or B (Figure 1), the available cycloSal-prodrugs are always obtained as mixtures of two diastereomers because of the newly formed chiral center at the phosphorus atom. The two diastereomers have different chemical and physical properties and possess different biological activity. In one particular case it was found that the RP-isomer of 3-Methyl-cyclo-Sal-d4TMP has a 10-fold higher activity than the SP-isomer.[3]
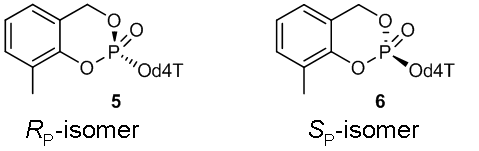 Figure 2: (RP)-3-Methyl-cycloSal-d4TMP 5 and (SP)-3-Methyl-cycloSal-d4TMP 6
Figure 2: (RP)-3-Methyl-cycloSal-d4TMP 5 and (SP)-3-Methyl-cycloSal-d4TMP 6 Sometimes the diastereomers can be separated chromatographically. However, this approach often fails. For this reason we are developing a diastereoselective synthesis route to yield diastereomerically pure cycloSal-prodrugs. One synthetical approach is based on the use of the chiral auxiliary 7, which causes an asymmetric induction at the phosphorus atom that leads to the preferred formation of the diastereomer (RP)-8. The following conversion of the diastereomer yields the diastereomerically pure cycloSal-prodrug (SP)-9 (Figure 3).[4]
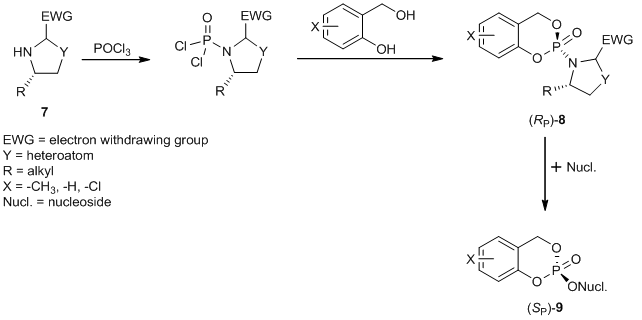 Figure 3: Diastereoselective synthesis of (SP)-cycloSal Nucleotide-Prodrugs
Figure 3: Diastereoselective synthesis of (SP)-cycloSal Nucleotide-Prodrugs
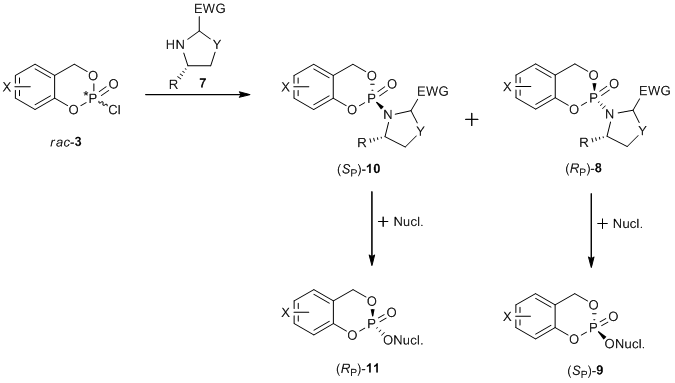
Another synthetical approach affords the synthesis not only of the (SP)- but also of the (RP)-cycloSal-prodrug. The chloridate rac-3 reacts with the chiral auxiliary under the formation of the diastereomers (SP)-10 und (RP)-8. After the column chromatography of the diastereomers, each individual reaction with the nucleoside analog leads to the diastereomerically pure cycloSal prodrug compound (Figure 4).[5]
Selected Publications
- C. Meier, cycloSal Phosphates as Chemical Trojan Horses for Intracellular Nucleotide and Glycosylmonophosphate Delivery-Chemistry Meets Biology, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 5, 1081-1102.
- C. Meier, M. Ruppel, D. Vukadinovic, J. Balzarini, „Lock-in“-cycloSal-Pronucleotides- A New Generation of Chemical Trojan Horses?, Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2004, 4, 383-394.
- C. Meier, cycloSal-Pronucleotides-Design of the Concept, Chemistry, and Antiviral Activity, Advances in Antiviral Drug Design 2004, 4, 147-213.
- a) E. H. Rios Morales, C. Arbelo Román, J. O. Thomann, C. Meier, Linear Synthesis of Chiral cycloSal-Pronucleotides, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 4397-4408. b) E. H. Rios Morales, J. Balzarini, C. Meier, Diastereoselective Synthesis of cycloSaligenyl-Nucleosyl-Phosphotriesters, Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 1649-1659
- E. H. Rios Morales, J. Balzarini, C. Meier, Stereoselective Synthesis and Antiviral Activity of Methyl-Substituted cycloSal-Pronucleotides, J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 7245-7252.
