Structure and Dynamics of Nucleic Acids
In recent years knowledge about new functionalities of RNA molecules increased dramatically. RNA molecules turned out to cover functions as catalysts (ribozymes and the ribosome), as gene expression regulators (riboswitches, siRNA and miRNA), or just as specific target binders named aptamers. In terms of academic and industrial collaborations (NOXXON GmbH) we investigate distinct and pharmaceutically relevant nucleic acids, and nucleic acid protein interactions, the structure, function and dynamics of functional RNA molecules, of natural RNA duplexes, tetra loops as well as structures of RNA in the L-configuration (Spiegelmer®) and of selected RNA racemates. As example for research highlights, the first RNA with natural sequence and none Watson-Crick Base Paaring was analysed to high resolution, as well al the first RNA in L configuration and a Racemate structure. Applying Resonanz Raman Spectroscopy at the Institute of Applied Physics (Prof. Rübhausen) we analyzed and observed for the first time electronic differences for the first time between the L and D configuration of selected RNA molecules. The reason for the homochirality observed in nature and the evolunationary selection of naturally occuring amino acids in proteins, to be in the L-configuration, and for ribose of DNA and RNA to be in the natural D configuration was still unknown. Due to their resistance to human nucleases, the non-naturally occurring L-nucleotides can be used as so-called Spiegelmers® (NOXXON GmbH, L-RNA aptamer) to design aptamers in mirror conformation which can bind with high affinity to therapeutically interesting molecules. In this context a complex of the Spiegelmer® NOX-E36 and its target, the pro-inflammatory chemokine CCL2, was analyzed to understand the distinct interactions. CCL2 is dysregulated in many diseases, for example, type II diabetes.
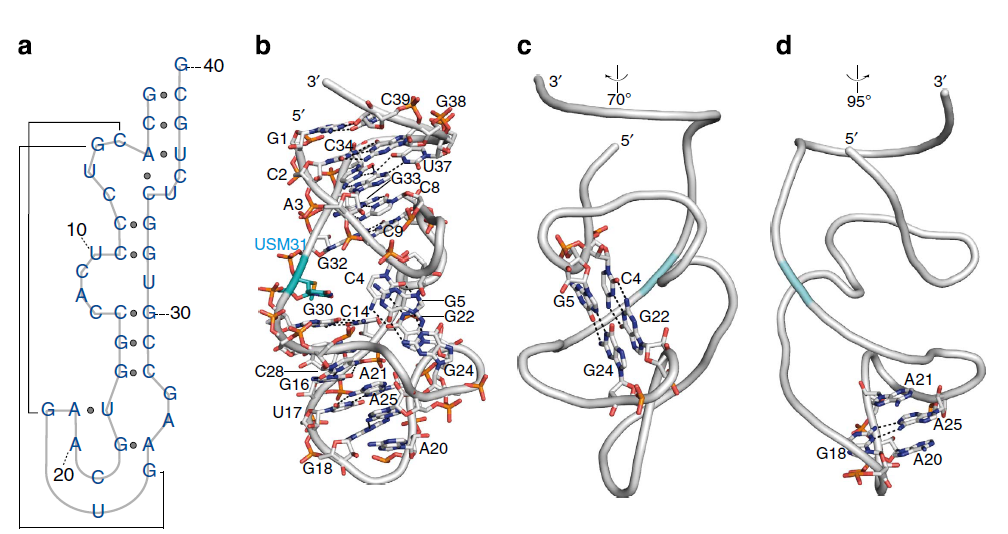
(a) Secondary structure of the NOX-E36-aptamer and (b) representation of the main intramolecular interactions of the L-oligonucleotide. (c) The pseudoknot-motif involving the base pairs C4-G22 (Watson–Crick) and G5-G24 (noncanonical) is highlighted. (d) A25 is flipped out of the helix and stabilized in this position through stacking between A21 and A20 and the noncanonical base pairing with G18
Selected References
- D. Oberthür, J. Achenbach, A. G. Gabdoulkhakov, K. Buchner, Ch. Maasch, S. Falke, D. Rehders, S. Klussann, Ch. Betzel: Crystal structure of a mirror-image L-RNA aptamer (Spiegelmer) in complex with the natural L-protein target CCL2. Nature Communications 6 , 6923 (2015).
- C. Förster, A. Eichert, D. Oberthür, C. Betzel, R. Geßner, A. Nitsche, J.P. Fürste: Features of "All LNA" Duplexes Showing a New Type of Nucleic Acid Geometry. J Nucleic Acids 2012, Article ID 156035 (2012).
- A. Eichert, D. Oberthuer, C. Betzel, R. Gessner, V.A. Erdmann, J.P. Fürste, C. Förster: The Seryl-tRNA synthetase/tRNASer acceptor stem interface is mediated via a specific network of water molecules. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 412 (4), 532-6 (2011).
- D. Oberthür, A. Eichert, V.A. Erdmann, J.P. Fürste, C. Betzel, C. Förster: The crystal structure of a Thermus thermophilus tRNA(Gly) acceptor stem microhelix at 1.6 Å resolution. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 404 (1), 245-9 (2011).
- A. Eichert, K. Behling, C. Betzel, V.A. Erdmann, J.P. Fürste, C. Förster: The crystal structure of an 'All Locked' nucleic acid duplex. Nucleic Acids Res 38 (19), 6729-36 (2010).
- A. Eichert, J.P. Fürste, A. Ulrich, C. Betzel, V.A. Erdmann, C. Förster: Superposition of two tRNASer acceptor stem crystal structures: comparison of structure, ligands and hydration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 395(3), 291-5 (2010).
- A. Eichert, J.P. Fürste, A. Schreiber, M. Perbandt, C. Betzel, V.A. Erdmann, C. Förster: The 1.2 Å crystal structure of an E. coli tRNA(Ser)acceptor stem microhelix reveals two magnesium binding sites. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 386 (2), 368-73 (2009).
- A. Eichert, M. Perbandt, A. Schreiber, J.P. Fürste, C. Betzel, V.A. Erdmann, C. Förster: Crystal structure of the human tRNAGly microhelix isoacceptor G9990 at 1.18A resolution. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 380 (3), 503-7 (2009).
- C. Förster, A. Zerressen-Harte, J.P. Fürste, M. Perbandt, C. Betzel, V.A. Erdmann: Comparative X-ray structure analysis of human and Escherichia coli tRNA(Gly) acceptor stem microhelices. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 368 (4), 1002-6 (2008).
- S. Bolik, M. Rübhausen, S. Binder, B. Schulz, M. Perbandt, N. Genov, V.E. Erdmann, S. Klussmann, Ch. Betzel: First experimental evidence for the preferential stabilization of the natural D- over the nonnatural L-configuration in nucleic acids. RNA 13 , 1877-1880 (2007).
- C. Förster, A.B. Brauer, S. Brode, J.P. Fürste, C. Betzel, V.A. Erdmann: tRNASer acceptor stem: conformation and hydration of a microhelix in a crystal structure at 1.8 Å resolution. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 63 , 1154-61 (2007).
